Discovery on a journey of Diabetes Management with our comprehensive guide. Explore holistic strategies, expert advice, and personalized diet plans for Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes management. Discover delicious recipes that enhance diabetes management and contribute to better blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Diabetes is a prevalent metabolic disorder that significantly affects how your body processes glucose (blood sugar). To effectively address this condition, it’s crucial to comprehend the various types of diabetes, identify common symptoms, and embrace suitable dietary strategies. This guide goes beyond conventional approaches by not only providing valuable insights but also incorporating delicious recipes into your routine. In this comprehensive guide titled “Diabetes Management,” we present you with a detailed overview of holistic diabetes management and encompassing home remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and expert guidance, along with meticulously tailored diet plans for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetes:

Referred to as “Madhumeh” in Hindi, diabetes is a multifaceted condition characterized by inadequate insulin production or ineffective insulin utilization in the body. Insulin, a vital hormone, plays a pivotal role in regulating glucose levels within your bloodstream. It facilitates the entry of glucose into your body’s cells, thereby supplying the energy necessary for their proper function. Through this guide, we aim to help you achieve mastery over diabetes by encompassing various medical and lifestyle approaches.
Types of Diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes: Problem with Insulin-Producing Cells

What is Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease where your body’s immune system attacks its own insulin-producing cells. Insulin is responsible for transporting glucose into your body’s cells to provide energy. When the insulin-producing cells are destroyed, glucose cannot enter the cells, leading to a significant increase in blood sugar levels.
Autoimmune Issue:
The primary issue in Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune response. Normally, your immune system defends against harmful bacteria and viruses. However, due to certain factors, the immune system malfunctions and starts attacking healthy cells, mistaking them for foreign invaders. In the case of Type 1 Diabetes, the immune system targets the insulin-producing cells.
Insulin Deficiency and Consequences:
When the insulin-producing cells are destroyed, the production of insulin decreases, and your body cannot effectively manage glucose. This leads to:
- High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Excess glucose accumulates in the blood, causing increased thirst, hunger, and frequent urination.
- Ketone Formation: In the absence of glucose utilization, the body turns to fats for energy, producing ketones, which can be harmful.
- Ketoacidosis: If ketone levels become too high, they can lead to the production of acids in the body, posing a severe health risk.
Impact on Children and Adolescents:
Type 1 Diabetes is commonly observed in children and adolescents, but it can develop at any age. While the exact cause is not known, some primary factors include:
- Birth Complications: Some theories suggest that natural complications at birth might trigger the onset of this condition.
- Genetic Influence: If someone in your family has Type 1 Diabetes, you might have a higher risk of developing it too.
- Diet and Environment: Poor diet and certain environmental factors could also contribute to the development of Type 1 Diabetes.
Management and Control:
Type 1 Diabetes is a lifelong condition, but proper management is possible:
- Insulin Therapy: Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes require insulin supplementation. This can be administered through injections or insulin pumps.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective management.
- Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine can help control blood sugar levels.
- Medical Guidance: Regular communication with your doctor and following their advice is essential.
Type 1 Diabetes is a challenging condition, but with proper management, you can lead a healthy life. Consistent adherence to proper diet, exercise, medication, and medical guidance is key to effectively managing this condition.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: Impact on Insulin Sensitivity of Cells
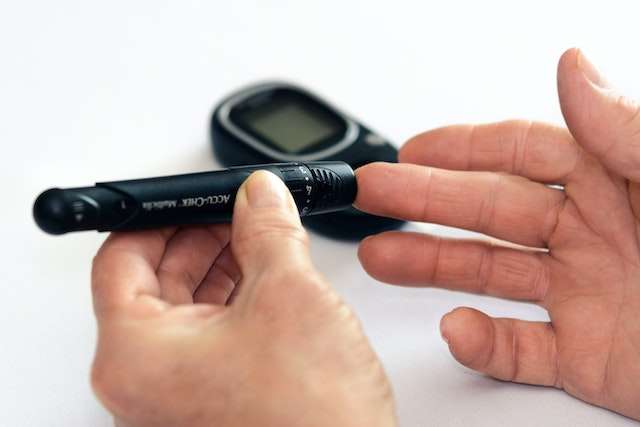
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 Diabetes is a common form of diabetes in which your body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. Insulin is a hormone responsible for transporting glucose (blood sugar) into your body’s cells, where it’s used as energy. In Type 2 Diabetes, insulin is produced, but your body’s cells do not use it effectively.
Effect of Insulin on Cells:
When you consume food, it gets converted into glucose, which increases in your blood after a meal. Insulin helps transport this glucose into your cells. However, in Type 2 Diabetes, the cells’ responsiveness to insulin diminishes, preventing proper glucose uptake by the cells. As a result, excessive glucose remains in your bloodstream.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to Type 2 Diabetes, with some primary ones being:
- Weight Gain: Excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant contributor to Type 2 Diabetes.
- Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, irregular sleep patterns, and a sedentary lifestyle increase the risk of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Genetic Influence: If Type 2 Diabetes runs in your family, it can increase your risk as well.
- Age: The risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes increases with age.
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol levels can also elevate the risk of developing diabetes.
Symptoms:
Some common symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Delayed wound healing
- Numbness or tingling
- Irritation or swelling
Management and Control:
To manage Type 2 Diabetes effectively, consider the following steps:
- Diet and Exercise: Consume a healthy diet and engage in regular physical activity. Include nutritious foods, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and protein in your diet.
- Weight Management: If you’re overweight, focus on weight control, as shedding excess pounds positively impacts blood sugar levels.
- Medication: Some individuals may require prescribed medications to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to make informed decisions about your management plan.
Type 2 Diabetes is often influenced by lifestyle choices, diet, and weight. By making positive changes in your lifestyle and adhering to your doctor’s recommendations, you can effectively manage this condition and lead a healthy life.
3. Gestational Diabetes:

This type occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes affect insulin utilization. It usually resolves after childbirth.
Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plans

1. Type 1 Diabetes Diet Plan:
In Type 1 Diabetes, your body cannot produce insulin, so you require insulin shots. Your diet plan will work in conjunction with insulin shots to maintain glucose at a normal level. Here’s a sample diet plan:
Breakfast:
- One cup of oatmeal or porridge.
- One bowl of fruit (such as apple, banana, or pomegranate).
- One glass of milk (preferably skimmed milk) or yogurt.
Lunch:
- One bowl of brown rice or multigrain roti.
- One bowl of vegetables (like okra, squash, or cauliflower).
- One bowl of lentils (such as red lentils, mung beans, or pigeon peas).
- Salad (tomatoes, cucumbers, spinach, etc.).
- A small bowl of yogurt.
Evening Snack:
- A small bowl of nuts (almonds, walnuts, pistachios).
- One fruit (like papaya, oranges, or pineapples).
Dinner:
- One bowl of vegetables or lentils.
- One bowl of quinoa, brown rice, or multigrain roti.
- Salad.
2. Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plan:
In Type 2 Diabetes, your body produces insulin, but your cells don’t use it effectively. Your diet plan will help regulate your blood sugar levels and keep you healthy. Here’s a sample diet plan:
Breakfast:
- One bowl of porridge or oats.
- One bowl of fruit (like apples, oranges, or papayas).
- One glass of milk (preferably skimmed milk) or yogurt.
Lunch:
- One bowl of brown rice or multigrain roti.
- One bowl of vegetables (such as spinach, okra, or cauliflower).
- One bowl of lentils (like masoor dal, mung dal, or toor dal).
- Salad.
- A small bowl of yogurt.
Evening Snack:
- A small bowl of sprouts or fox nuts.
- One fruit (like pears, guavas, or peaches).
Dinner:
- One bowl of vegetables or lentils.
- One bowl of quinoa, brown rice, or multigrain roti.
- Salad.
Note: These diet plans are illustrative examples. Each person’s body is unique, so it’s essential to consult your doctor before creating a diet plan. You need to carefully balance carbohydrates, protein, fats, and fiber to maintain controlled blood sugar levels.
Home Remedies for Diabetes Management
Home remedies can be helpful in managing diabetes, but it’s important to consult your doctor before using any remedy. Here are some suggested home remedies for individuals with diabetes:
Bitter Gourd (Karela):
Consume bitter gourd juice or make a paste by soaking and grinding bitter gourd in water. Bitter gourd is beneficial for diabetes management as it helps control blood sugar levels.
Fenugreek Seeds (Methi Dana):
Soak fenugreek seeds in water overnight and consume them on an empty stomach in the morning, or use fenugreek seed powder. Fenugreek seeds are known to lower blood sugar levels.
Black Plum (Jamun):
Make a powder from dried jamun seeds and consume it. Jamun seeds contain anti-diabetic properties that help in reducing blood sugar levels.
Neem Leaves (Margosa):
Boil neem leaves in water and drink the water. Neem leaves have anti-diabetic properties that assist in controlling blood sugar levels.
Aloe Vera:
Aloe vera juice might be useful in diabetes management, but consult your doctor before using it.
Cinnamon (Dalchini):
Cinnamon can be beneficial for diabetes management. You can incorporate cinnamon in your diet or mix cinnamon powder in water and consume it.
Turmeric (Haldi):
Include turmeric in your meals. Turmeric’s antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties can help lower blood sugar levels.
Exercise:
Regular physical exercise aids in diabetes management. Exercise increases the impact of insulin and helps maintain blood sugar levels.
Dietary Awareness:
Consume nutritious foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Avoid refined carbs and processed foods.
Stress Management:
Stress can affect diabetes. Practice techniques like mindfulness and deep breathing to reduce stress.
Remember to consult your doctor before trying any of these home remedies. Following your doctor’s advice and recommendations is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Delicious Diabetic-Friendly Recipes:
Diabetes Management Recipes
1. Oats and Fruit Parfait:
- Cook oats in milk and let them cool.
- Layer oats, chopped fruits (such as pomegranate, banana, or berries), and yogurt in a glass.
- Add a drizzle of honey or stevia, if desired.
2. Vegetable Pulao:
- Soak brown rice and then cook it.
- In a pan, sauté cumin seeds, cloves, and cardamom pods in a little oil. Add finely chopped onions and sauté.
- Add mixed vegetables (like carrots, cauliflower, beans), salt, and sauté.
- Mix in the cooked rice and cook on low heat.
3. Spinach and Cottage Cheese Salad:
- Blanch spinach leaves in boiling water, then cool them in ice water.
- Cut cottage cheese into small cubes.
- Chop the blanched spinach, add cottage cheese and diced tomatoes.
- Add a pinch of salt, black pepper, lemon juice, and fresh coriander leaves.
4. Masoor Dal Khichdi:
Ingredients: Masoor dal (red lentils), rice, vegetables (radish, carrot), asafoetida (hing), cumin (jeera), salt.
- Boil rice and masoor dal together.
- Add vegetables and spices, then cook thoroughly.
5. Oats Dosa:
Ingredients: Oats, rice flour, yogurt (curd), green chili, ginger, salt.
- Blend oats and mix with rice flour.
- Add yogurt, green chili, ginger, and salt.
- Cook the mixture on a dosa pan.
6. Methi Thepla:
Ingredients: Fenugreek flour (methi atta), gram flour (besan), yogurt (dahi), turmeric (haldi), coriander (dhaniya), salt.
- Knead all ingredients together.
- Make dough.
- Roll out flatbreads (thepla) on a griddle.
These dietary tips and delicious recipes can play a significant role in managing your diabetes. However, remember that a balanced lifestyle, regular exercise, and proper medication (if prescribed) are also essential components of effective diabetes management.



Greetings from Colorado! I’m bored to death at work so I decided
to browse your site on my iphone during lunch break.
I love the information you present here and can’t wait to take
a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how quick your blog loaded on my phone ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, fantastic blog!